Connect with us
Published
2 months agoon
By
admin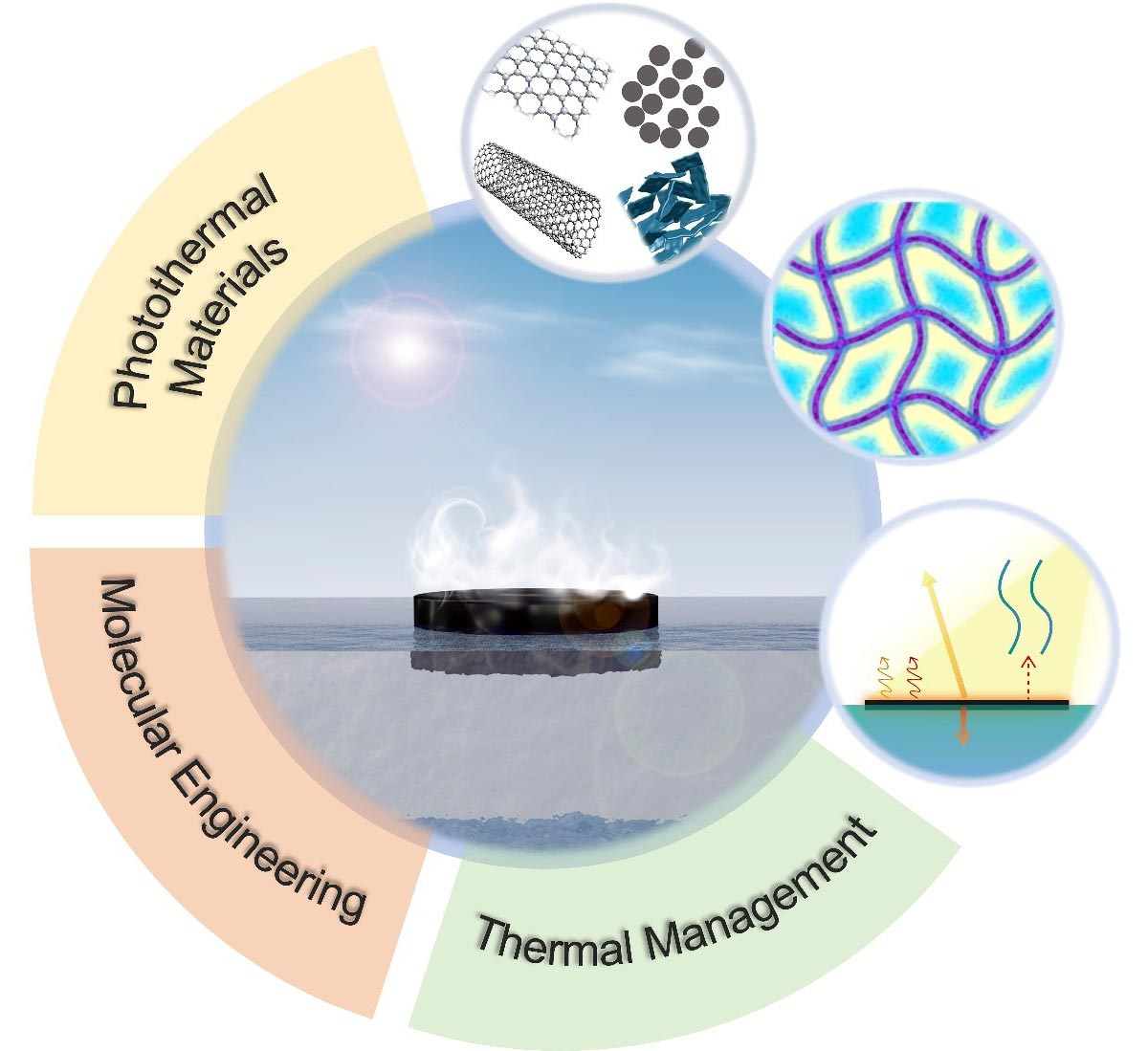
Interfacial solar evaporation (ISE) is an emerging desalination technology that utilizes solar energy for sustainable water purification. A recent review study published in Nano Research Energy outlines strategies for developing efficient ISE systems to address global freshwater shortages. Researchers suggest five key recommendations: introducing new energy sources to enhance system reliability regardless of solar intensity, exploring advanced photothermal materials for improved thermal energy utilization, creating innovative designs for photothermal evaporators to optimize energy harvesting and water evaporation, focusing on effective water production techniques in limited spaces, and developing scalable ISE systems for broader applications like seawater desalination and wastewater treatment.
Compared to traditional desalination methods that heavily rely on fossil fuels, ISE offers a greener alternative by minimizing energy loss and maximizing heat conversion efficiency. Researchers highlight that advancements in ISE technology could significantly increase evaporation rates and overall performance. While the potential for ISE in combatting clean water scarcity is recognized, experts emphasize the need for further research and development to transition these technologies into practical applications.













