Connect with us
Published
2 months agoon
By
admin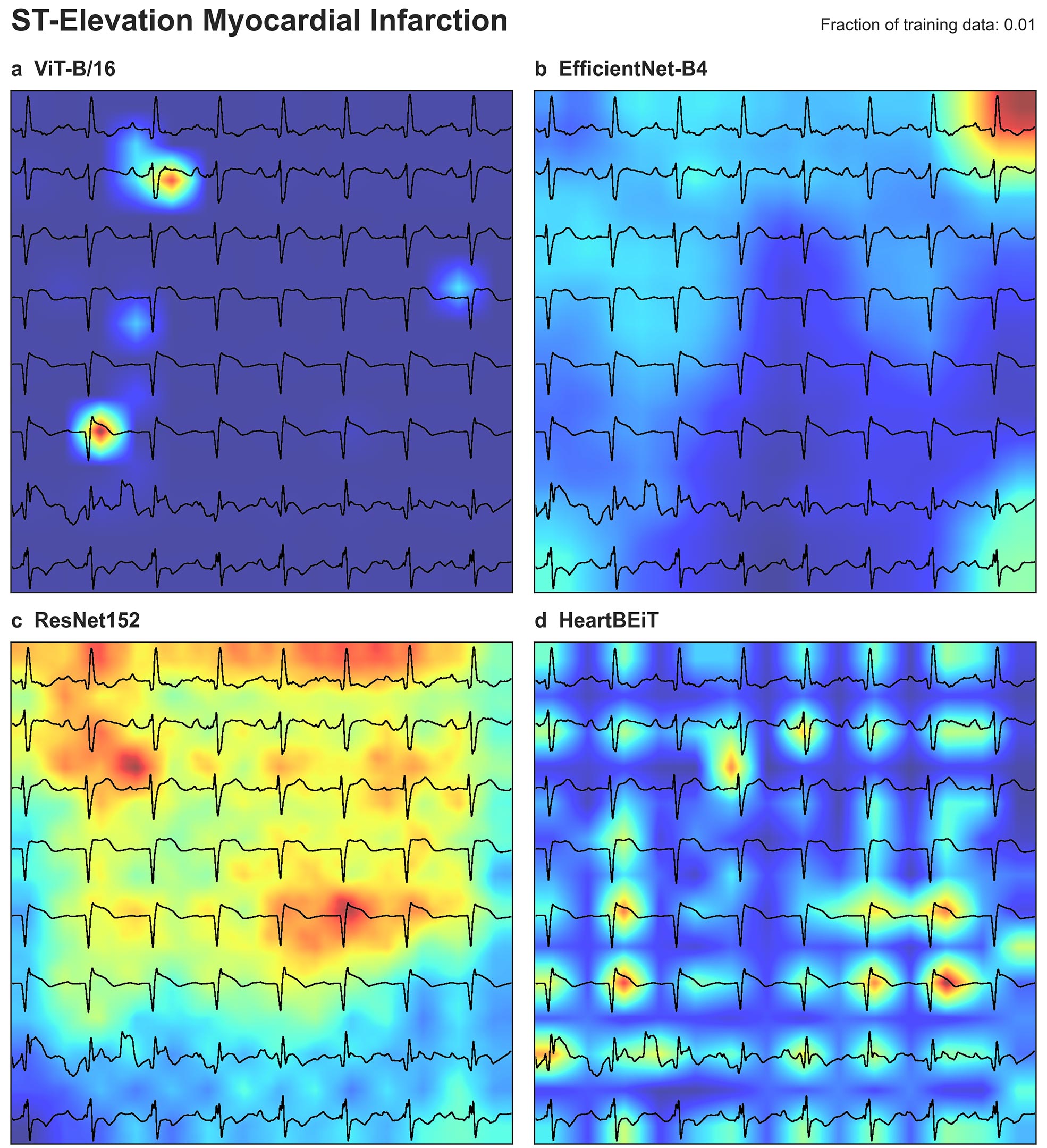
Mount Sinai’s HeartBEiT is a groundbreaking AI model designed to enhance the accuracy of electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis, particularly for diagnosing heart attacks and rare cardiac disorders. This innovative approach interprets ECGs as language, allowing the model to outperform traditional convolutional neural networks (CNNs), especially in diagnosing conditions with limited data. In a recent study published in npj Digital Medicine, researchers demonstrated HeartBEiT’s superior performance compared to established methods, achieving accurate diagnoses using significantly less data.
The model was trained on 8.5 million ECGs from 2.1 million patients, which enabled it to effectively analyze specific ECG regions related to cardiac issues, providing clinicians with clearer insights. Unlike conventional CNNs, which often act as “black boxes,” HeartBEiT offers better “explainability,” enhancing clinical understanding of ECG results.
Researchers emphasize that while HeartBEiT significantly augments ECG analysis, it is not intended to replace human diagnosis. Instead, it serves as a powerful tool for improving the detection and monitoring of heart conditions, navigating the limitations often faced with ECG interpretations. The study was funded by the NIH and highlights a vital step forward in integrating AI into clinical cardiology for more precise patient care.

















